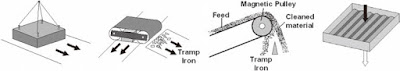
Mineral processing-Electrical separation
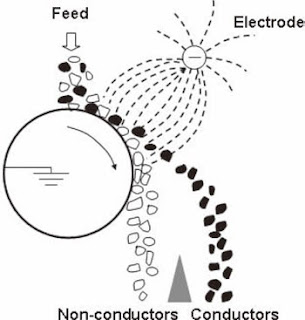
If an ore contains conducting as well as non-conducting minerals/particles, electrostatic separation or high tension separation can be employed. Theoretically, it is not necessary that one of two minerals should be a good conductor and the other be a poor conductor, but the difference in their conductivity will affect the separation. The basis of any electrostatic separation is the interaction between an external electric field and the electric charges acquired by the various particles. Particles can be charged by: 1 Contacting dissimilar particles. 2 Conductive induction. 3 Ion bombardment. In every separation, two or more charging mechanisms occur. In charging by contacting dissimilar particles, particles placed on surface are made to repeatedly contact one another as well as the surface; the surface will acquire electrons from one type of particles and give electrons to another type so that two types of particles are charged with opposite charges. When they are passed t