Mineral processing unit operation and examples
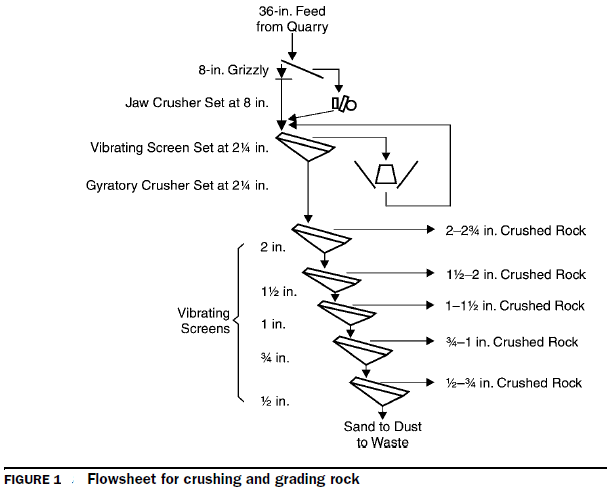
UNIT OPERATIONS In mineralprocessing plant , Numerous steps, called unit operations, are involved in achieving the goal of extracting minerals and metals from ores in their purest possible form. These steps include Size reduction . The process of crushing and grinding ores is known as comminution. The purpose of the comminution process is threefold: (1) to liberate valuable minerals from the ore matrix, (2) to increase surface area for high reactivity, and (3) to facilitate the transport of ore particles between unit operations. Size separation. Crushed and ground products generally require classification by particle size. Sizing can be accomplished by using classifiers, screens, or water elutriators. Screens are used for coarse particulate sizing; cyclones are used with fine particulates. Concentration . Physicochemical properties of minerals and other solids are used in concentration operations. Froth flotation, gravity concentration, and magnetic and electrostatic co