Beneficiation Processing of Iron ore
Beneficiation
Processing of Iron ore
Sinonine deeply know that most prominent
ore found in world are mainly hematite and magnetite. Among these, hematite is
considered to be most important. Iron ore is used in production of pig iron
which is further used in production of steel other uses of iron ore are like
industrial finishes, polishing compounds and sponge iron industries. Iron ore
belongs to Precambrian stage and its deposit is present in massive, laminated,
friable and also in powdery form.
Hematite
Hematite is most important iron ore
mineral main source for industries. Its composition is Iron Oxide and sometimes
slight amount of titanium. Its name comes from the Greek word for blood, haima,
because of its reddish colour. Crystals occurs in thin plates, as well as
bundles of small micaceous plates, and in thin splinters. Most commonly
massive, mammilary, botryoidal, reniform, oolitic, stalactitic, and radiating.
Scalenohedral and rhombohedral crystals occur, although infrequently, and
dendritic and rosette forms are also found. Hematite may also form as a
pseudomorph of other minerals, especially as octahedral crystals of Magnetite.
Striking features are reddish streak, hardness, crystal habits and Para
magnetism. It becomes strongly magnetic when heated. Its specific gravity is
4.9 to 5.3 and luster is metallic to dull. Hematite is weakly magnetic, but it
has a variety called magnetite which is found in many ore bodies in minute
quantities having magnetic properties closely related to those of magnetite.
The content of iron in the ore and physical characteristics vary from place to
place in different types of ores.
Magnetite
After hematite, magnetire is second most
abundant Iron bearing ore. Black magnetic oxide of iron crystallizing in the
isometric system with hardness of 5.5 to 6.5. Magnetite ore is of little value
in its raw state, but it offers considerable advantages in its concentrated
form. These include providing a viable iron-making commodity for premium
quality steel production. By comparison, magnetite ore typically has much lower
iron content when mined of between 25%
and 40% Fe and in this form is unsuitable for steel making. The main iron
mineral in magnetite ore is the ferrous iron oxide magnetite (Fe3O4). Magnetite
ore requires complex processing to separate magnetite minerals from other
minerals in the ore to produce an almost pure magnetite concentrate with an
iron content of between 68% Fe and 70% Fe that is highly sought after by steel
makers. It also occurs as a replacement product in sedimentary or metamorphic
rocks. It is found as placer deposits as ―black sand‖ in beach deposits and as banded layers in
metamorphic and igneous rocks.
Processing
of Iron ore
Iron processing depend mainly on the type
of ROM ore feed and optimum product. Dry screening into lumps and fines is
practised for high quality flaky ore and blue dust, because, if wet treatment
is used, a substantial part of good quality material is rejected in the form of
slimes. Another advantage of dry screening is dry screened fines also retain
ultra-fines particle may later be used in sintering. Ore types having gangue
material which strictly adhere to the useful metal surface are subjected to wet
screening -> classification or scrubbing -> wet screening ->
classification. Mineral processing plants at mines usually use dry screening
for direct ore mined from the face.
Part of plants use wet screening -
classification for ores that meet the cut off criteria. Scrubbers are being
used in some beneficiation plant for better recovery. Some mines have hydro
cyclones , screw classifiers for better beneficiation process . Log washers are
also being used to produce better and stable quality lumps of iron ore in some
mines. Various techniques and methods generally being used in iron ore processing
are schematically shown in the figures below.
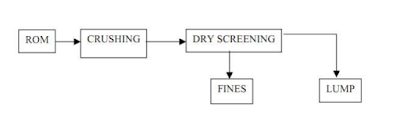
Fig 1 Dry
screening process
Fig 2 Wet
screening classification
Fig 3
Scrubbing wet screening classification
Fig 4
Washing and gravity separation process
Slimes
of Iron ore
For improving quality and to reduce cost
of production iron ore industries are demanding high grade raw minerals.
However, the ore being a non-renewable natural resource, the reserve of good
quality ore is depleting. Marginal to sub-marginal ore should be used to meet
the present as well as future requirements and avoid environment related
problems. The circumspect utilization of Iron ore can conserve high grade
mineral resource. So today there is need of sustainable development in iron ore
mining that is need of present without compromising the need of future
generation. So it becomes vital to develop some technique for beneficiation of
unutilized low grade ore and ultra-fine material i.e. slime. Washing plant data
implies that generation of slime comprise of 30-35% of the total ore mined.
Because of lack of technology and its complex nature, a significant quantity of
slime remains unused. These slimes are dumped which causes environmental
hazards. If pellets are produced directly from such fines, they become high in
alumina which is undesirable in Blast furnace as high alumina content will
adversely affect the pellet properties, typically measured by Reduction
Degradation Index (DRI) and Reducibility Index (RI). A drop in alumina content
can improve these properties and also reduce the coke consumption in Blast
furnace. Tailings contain harmful material like iron sulphide which is primary
source for acid mine drainage. Sedimentation test show that the tailings and
the area required for tailing pond is around 3155 m 2 in comparison to 10,000
m2 obtained from the use of an empirical equation. It is
very difficult to evaluate the characteristics of these slimes where
most of the particles are below 50 microns. Base on the fact that iron ore
production wills more than double and rise to at least 300 million tonnes soon,
finding suitable methods of safe disposal/utilization of slimes is indeed
urgent. If we look at the present quantity of the iron ore slimes that is being
generated annually, amalgamation of quantity of slimes, over the years the fact
that slimes are available in ground form and assaying that is reasonably high
%Fe, it is natural that if beneficiated in a proper way, these slimes can be
considered a national resource rather than a waste. The alumina content of the slimes,
if brought to less than 2% Al2O3 in the beneficiated product will
---Lead to better utilization of national
resources.
---Achieve more mine output (enhanced
production) with not much additional costs.
---Reduce environmental issues associated
with storage and disposal of slimes.
---Result in higher blast furnace and
sinter plant productivity.
In view of the above facts proper
technology shall be adopted for processing of slimes to recover iron ore values
from them, this will be a step forward for conservation of mineral in national
interest. As particle size in slime is finer (<.15mm) so it will be easy to
beneficiate
the slime without the use of any
combination process.
In last twenty years importance is slowly
tilting towards slime beneficiation and in addition to the traditional methods
of processing, enhanced gravity separators (EGS) such as Falcon, Knelson
concentrator are also being experimented with to beneficiate the Slimes. Now aday’s
novel method of beneficing iron ore slime is used via magnetic and gravity
method ofseparation.
Two distinct mineral constituent of
Alumina iron ore slimes are gibbsite (hydrated aluminium oxides) and kaolinite.
Exact amount of alumina has not been quantified till date according to
liberation studies a significant portion of alumina is present in the liberated
form and so it is possible to separate them using physical methods. Slag
viscosity in blast furnace is increased due to high alumina content. This leads
to increase in metal loss in slag, increase in thermal requirement and thus
makes the Blast furnace operation more tough. To reduce alumina burden new
technologies are adopted by steel industries. Using pellets can reduce this
burden.
All around the world Iron ores are being
beneficiated,Several Methods such as
---Spiral
---Floatex density separators
---Jigs
---3 multi-gravity separator
---Low and high intensity magnetic
separator
---Conventional as well as column
flotation
---Selective dispersion
---Flocculation is all part of current
industrial practice.





评论
发表评论