Gravitational classifiers
In mineral processing plant , Two basic types of gravitational classifiers employed today
are the spiral classifiers and the
rake classifier. They both introduce the feed submerged into a pool area and
subject the solids to an upflow current. The overflow is obtained from a
peripheral weir that provides the vertical velocity. A solid whose terminal
settling velocity is high enough will settle against this current and report to
the base of the pool. At this point, a rake or screw conveys the solids out of
the pool and up the beach to drain the “sands” product before discharging it
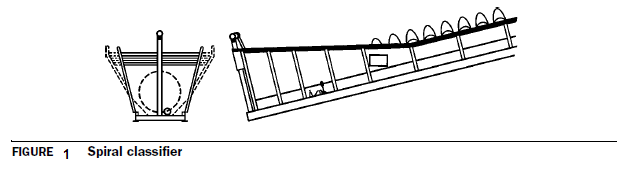
over the end of the slope. Figure 1 is a schematic of a spiral classifier. The
rake classifier has a series of rakes (actually blades) that operate in a
reciprocating fashion to move the sands up the beach.
A third
type is termed a “hydroseparator.” The feed again enters submerged through a
circular centralized feedwell, and the peripheral overflow weir causes an
upward velocity. The underflow is raked toward the central outlet and is pumped
out. The unit looks much like a conventional gravitational thickener or clarifier except that the unit is shallower and the
bottom slope is usually steeper. The speed of a rake mechanism is normally two
or more times that of a thickener, because of the more granular nature of the
solids and the higher solids rate per unit area.
The main
advantage of the rake and spiral classifiers is their higher percent solids of
the sands product, because the product is drained. The hydroseparator has the
advantage of higher capacity from a single unit as it uses a much larger pool
area. The hydrocyclone is a widely
used classifier that employs centrifugal force.
sinonine can also provide sand washing plant epc.
sinonine can also provide sand washing plant epc.

评论
发表评论